What is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that often lead to increased pressure within the eye due to a buildup of fluid. This elevated pressure can gradually damage the optic nerve.
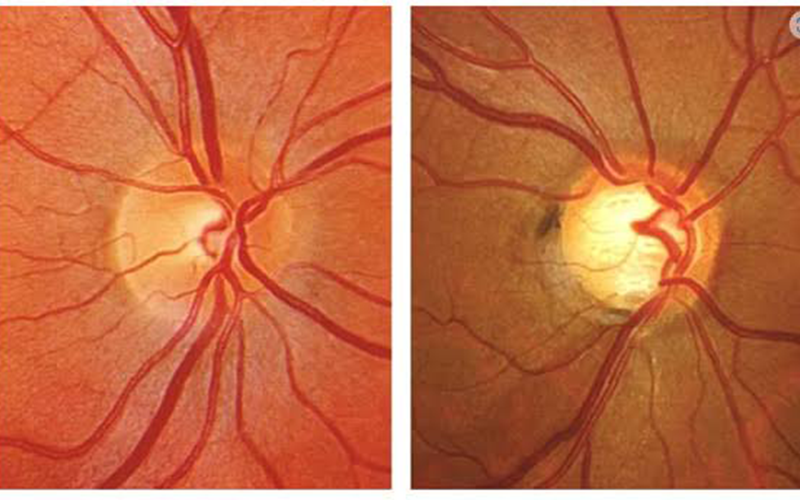
The optic nerve, which transmits visual information to the brain, consists of over one million delicate nerve cells. Though each cell is several inches long, it is extremely thin—about one twenty-thousandth of an inch in diameter. When pressure in the eye rises, it compresses these nerve cells, causing damage and eventually leading to their death. This process results in permanent vision loss. However, early detection and treatment of glaucoma can help protect the optic nerve and prevent vision impairment.
Who is at Risk?
Glaucoma is a serious condition that affects people of all ages, from infants to seniors. Regular eye check-ups are essential, as early detection and treatment are the only ways to prevent vision loss and blindness caused by glaucoma.
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing glaucoma, including:
People who have:
- Diabetes
- Myopia (nearsightedness)
- Regular, long-term Steroid/Cortisone use
- A previous eye injury
- Migraine, poor blood circulation or other health problems affecting the whole body.
What Are the Symptoms of Glaucoma?
Open-angle glaucoma
Open-angle glaucoma often develops without any warning signs or noticeable symptoms in its early stages. Over time, blind spots may begin to appear in peripheral (side) vision.
Most individuals with open-angle glaucoma remain unaware of vision changes until significant damage has occurred, earning it the nickname "silent thief of sight." Regular eye exams are essential for early detection, allowing your ophthalmologist to identify and manage the condition before vision loss occurs.
Angle-closure glaucoma
People at risk for angle-closure glaucoma typically have no symptoms prior to an attack. However, early warning signs may include blurred vision, halos around lights, mild headaches, or eye discomfort. If these symptoms occur, it is important to consult an ophthalmologist promptly.
During an angle-closure glaucoma attack, the following symptoms may appear:
Normal Tension Glaucoma
Normal tension glaucoma occurs when eye pressure is within normal limits, yet signs of glaucoma are present, such as blind spots in vision and optic nerve damage.
Glaucoma Suspects
Individuals with higher-than-normal eye pressure, known as ocular hypertension, but no signs of damage are considered "glaucoma suspects." They are at a higher risk of developing glaucoma over time and require close monitoring by an ophthalmologist.
Diagnosing Glaucoma
Early detection is crucial, even before symptoms appear. Various diagnostic tools help in identifying glaucoma, including:
- Tonometer: Measures eye pressure.
- Visual Field Test: Identifies blind spots.
- Ophthalmoscopy: Examines the optic nerve for damage.
Treating Glaucoma
Treatment options include eye drops, oral medications, laser surgery, eye operations, or a combination of methods. The primary goal is to prevent further vision loss, as damage caused by glaucoma is irreversible. Maintaining controlled intraocular pressure (IOP) is essential to safeguarding vision.


